The meaning of the word cancer involves abnormal uncontrollable cell growth, with the ability to spread to other parts of the body. The rapid cell growth allows the cancer to grow stronger against your body’s defence mechanism and potentially become fatal. To many people, cancer does not quite mean abnormal and uncontrollable cell growth; to them it only means death. It brings them a great deal of stress and it almost seems unbeatable. Cancer seems like a bully that just comes around to antagonize people in unfortunate situations. It does not seem to ever affect the wealthy or powerful individuals, however this may not be the case.
As an avid sports fan that marvels after all the athletes on television, I would ever think that cancer could affect any of them, but its more common then you think; just ask Mario Lemieux and Eric Berry. Both of these athletes were diagnosed and survived a form of cancer called Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. This particular form of cancer has to do with blood cells and in this case a specific type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. The primary focus of this review is to illustrate the main causes of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma and methods of treatment. A British physician named Thomas Hodgkin first described Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in 1832. This white blood cell disease is mostly common in Males ages over 45 that show symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes. The disease is identified by the systematic spread of disease from one lymph node unit to the next by the expansion of orderly symptoms. While examining this disease the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells are the characteristic of the findings (van den Berg et al. 1999).
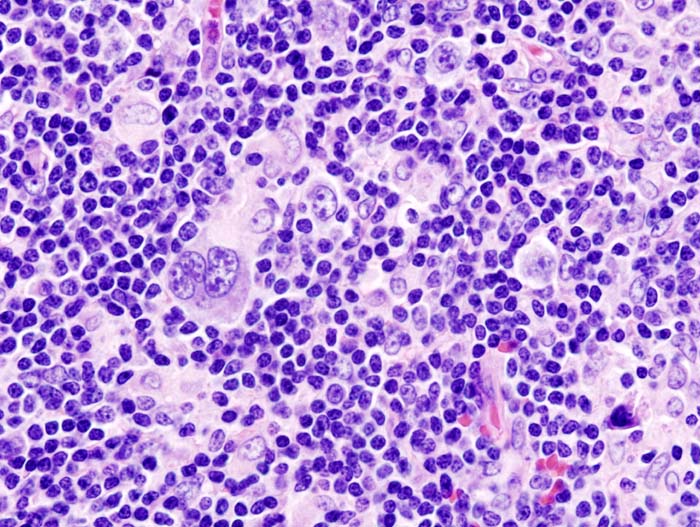
Figure 1. Illustration of oversized Red-Sternberg Cells (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported photo taken by NGH)
Rigorous analyses of the disease causing patterns has recently indicated that an infectious perpetrator as being responsible for the potential cause of this disorder. This infectious virus is called the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) which is thought to be the cause of the rapid growth of the Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells (Thomas et al. 2006). Patients with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma who are also positive with EBV show an increase of expression of T-cell lymphoma genes. These genes include LMP1, LMP2a, and EBNA1 (Thomas et al. 2006). The Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells have also displayed apoptosis immunity; the reasoning for this is still undetermined due to the fact that mutations affecting p53 or Fas genes are unlikely events in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma cells (Thomas et al. 2006). Research has shown that expression of EBV latent genes, in cases where EBV and Hodgkin’s Lymphoma are both present, could be involved in transformation by up-regulation of a certain transcription factor (van den Berg et al. 1999). Researchers also have discovered that HRS cells can add to the ineffective immune response. They do this by expressing immunosuppressive cytokines that attract the cells that immune to the bodies defence mechanism (van den Berg et al. 1999).
The first treatment in the medical world for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma was MOPP; a team of four drugs that are pooled together to attack the infected lymphocytes. The treatment consists of four-week intervals that last for 6 cycles (Hutchings et al. 2006). The treatment was developed in the 1960s, to date this form of chemotherapy is not used initially to combat Hodgkin’s Lymphoma but is often used as a back up for the sake of patients who may have allergies. Now ABVD is the treatment of choice and this also consists of a four-drug procedure. This strenuous treatment takes up six to eight months depending on the severity of the tumour (Hutchings et al. 2006). There are other treatment options available but they come with elevated risk; some even breaking major heath guidelines (ie. Stanford V).
It is quite devastating how you could be the worlds best hockey player and in a blink of an eye, it all changes. Cancer does not have any morals; it will go after anyone. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, in particular, is very treatable but unfortunately the specific mechanism that causes it is still not fully discovered. With the discovery of the mechanism, scientists will be able to synthesize a whole new regime of drugs to target Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
Recent Comments