Diabetes can lead to serious complications over time if left untreated. If patient is diagnose with type II diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin and the body is resistant to the insulin that is produced. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use blood sugar known as glucose for energy. The body takes the food and breaks down carbohydrates into glucose for energy. Insulin is essential to help get into the body’s cells. What causes type II diabetes? Obesity and physical inactivity are the main causes of type II diabetes. Type II diabetes can also be caused by inherited genetic factors or lifestyle habits.
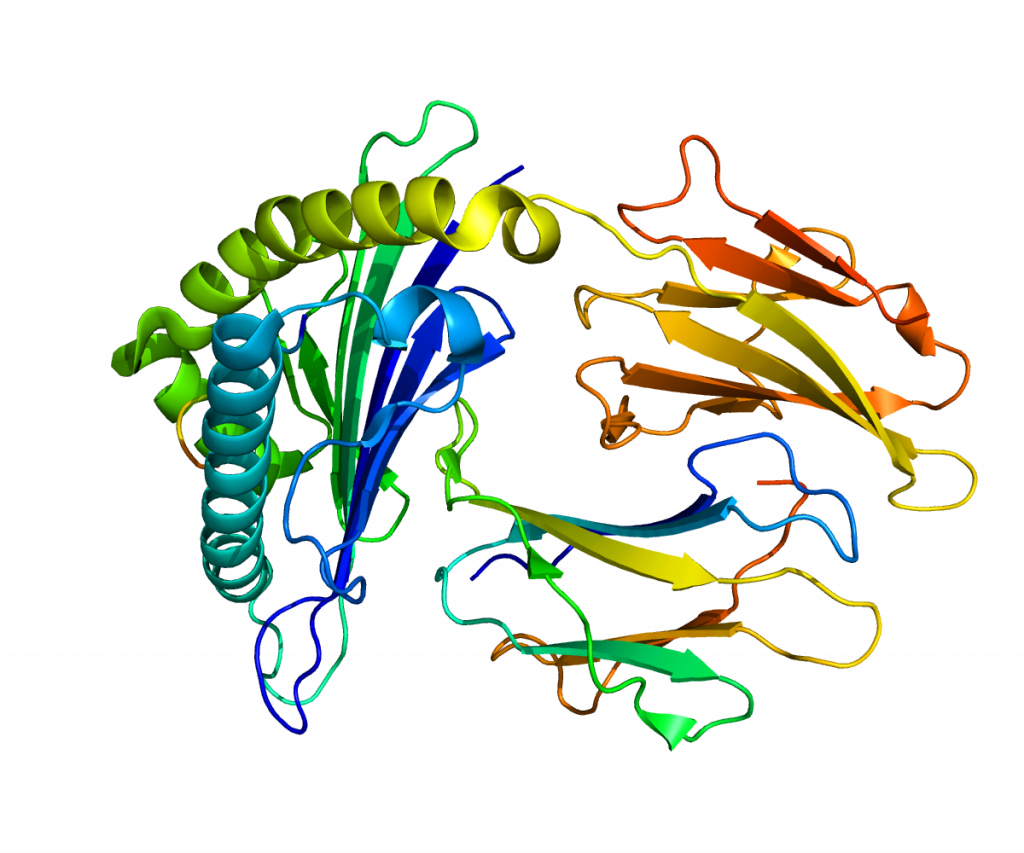
Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) mediate the control of various cellular processes by insulin. In general, it phosphorylates insulin. However, when IRS2 is mutated, it can lead to type II diabetes. Using mice as a subject, Dr. Withers and his team performed this experiment whether mutated IRS2 mice were insulin resistant. It turned out that mutation of IRS2 caused the development of type II diabetes. The mutated IRS2 mice exhibited insulin resistance and β-cell deficiency which prevents adequate compensation. This caused glucose to accumulate in the extracellular space and increase glucose levels in the blood. This indicates that the mutation of IRS2 may contribute to the pathophysiology of human type II diabetes.
Insulin receptor substrate (IRS2). Photo credit Pleiotrope. (Public Domain)
Islet β-cell failure for insulin resistance causes type II diabetes. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a risk factor for the development of type II diabetes and affects islet β-cell. There was a study of 358 Asian patient have NAFLD at baseline and later diagnosis of type II diabetes after 6 years. Many tissues of the body like skeletal muscle and cardiac tissue respond to over-nutrition with protective responses to prevent nutrient-induced toxicity by developing insulin resistance. Which means islet β-cell need to adapt this situation, enabling partitioning of excess nutrients to safe storage within adipose tissue. Islet β-cell failure happens when a patient with islets is susceptible to damage from genetic or acquired defects. Once that happens, hyperglycemia, high blood sugar, and hyperlipidemia, high concentration of fats or lipids, develop. In order for β-cell to work, insulin secretion needs to be adjusted for insulin sensitivity. This is done by calculating the ‘disposition index’ by multiplying a measure of insulin secretion by a measure of insulin sensitivity.
Obesity is one of many risk factors for type II diabetes. Around 90% of people with type II diabetes have obesity. People with type II diabetes do not produce enough insulin to overcome the insulin resistance because a fat tissue prevents insulin from doing its job. Weight lost is very important in the management of type II diabetes.
This graph is showing the increase of body mass index which increases the risk of having type II diabetes. (Image credited: MyHealthyWaist, CC)
There are many treatments for type II diabetes. Two are pretty obvious: eating healthy and physical activities. Your diet should have high-fiber, low-fat foods like fruits, vegetable and whole grains and less animal products. Fiber controls blood sugar and reduces the impact of carbohydrates. The glycemic index is a scale that ranks carbohydrates based on the impact they have been raising blood levels after eating. Low glycemic index foods stable blood sugar while high glycemic index food raise the blood sugar fast. Exercising help prevent or delay type II diabetes from developing. It improves your body’s sensitivity to insulin and helps manage your blood glucose levels. Aerobic exercises like jogging should help control blood sugar more effectively. Make sure you check your blood sugar time to time and remain with the target range; it can be unforeseeable. Now don’t be a couch potato and go outside and explore the world!
Lastly, here’s the message from Wilford Brimley about diabetes.


Recent Comments